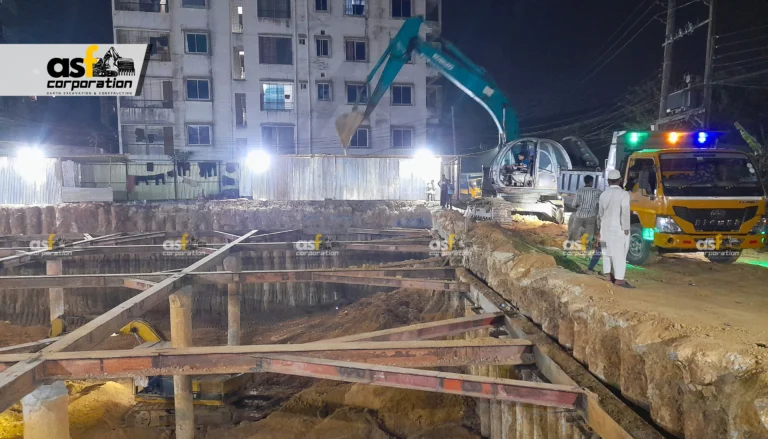
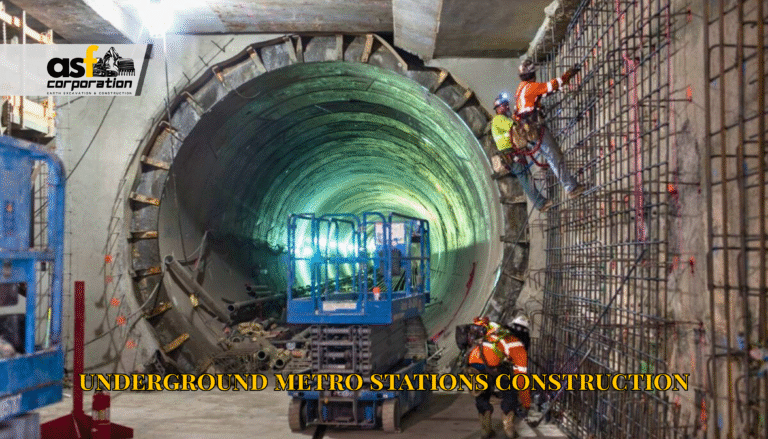
In the world of construction and civil engineering, the foundation of any structure is quite literally where everything begins. Among the various excavation techniques available to construction professionals, the open cut method stands out as one of the most fundamental and widely used approaches. Whether you’re planning a residential project or overseeing a commercial development, understanding this excavation technique can help you make informed decisions about your construction process.
What is the Open Cut Excavation Method?
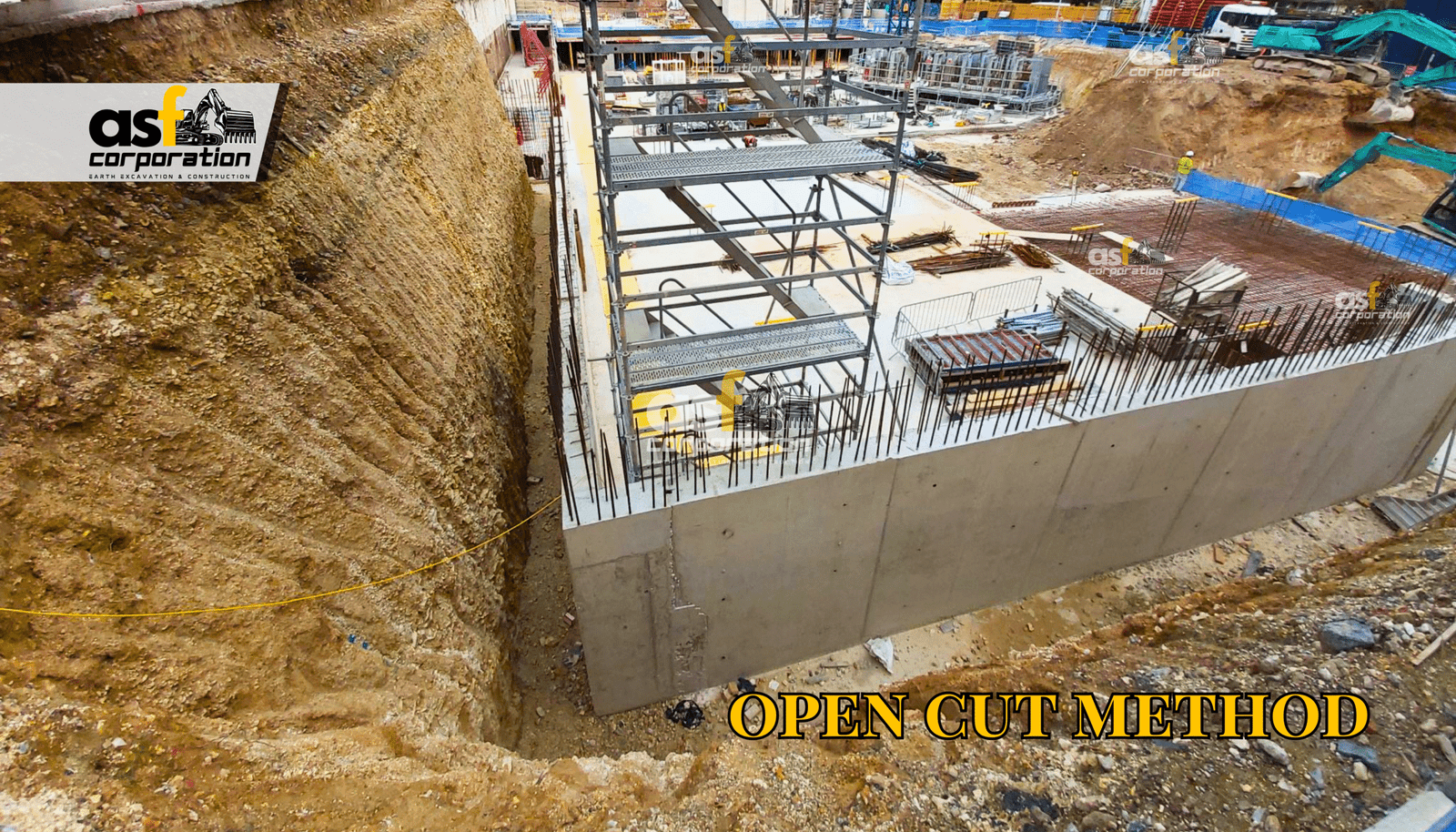
The open cut excavation method is a technique that involves removing massive amounts of earth from a worksite at the beginning of the construction process. This excavated area becomes the site for a building’s foundation and, when applicable, its basement. Unlike the top-down construction method, which begins with vertical cuts for foundation walls followed by an upward build (with basement excavation occurring later), the open cut method prioritizes basement excavation first, with the building constructed upward from there.
This approach is particularly common for tunnel or underground structure construction, especially for shallow buried projects. As the name suggests, it requires opening up the ground surface to the required depth, completing the construction work, and then backfilling to restore the surface.
Types of Open Cut Excavation
There are two primary types of open cut excavation methods, each with its own applications and benefits:

Open Cut Slope Method
The open cut slope method involves digging along foundation walls and spreading the dirt in a sloped pile from the structure. This creates a natural slope that runs up the sides of the area, starting from ground level down to the base of the foundation. The key advantage of this approach is that the slope’s natural properties reduce or eliminate the need for retaining walls.
This method works exceptionally well for:
- One-story and two-story buildings
- Structures with shallow basements
- Projects where cost-effectiveness is a priority
- Situations where basic physics can protect the foundation from collapsing soil
Open Cut Cantilevered Method
The cantilevered open cut method utilizes retaining walls to support the excavation sides. This approach is more suitable for:
- Taller buildings
- Structures with deeper foundations
- Buildings with multi-level basements
Depending on the soil strength surrounding the building, deep open cuts may benefit from bracing systems. These systems transfer weight from the retaining wall to horizontal struts installed in front of the wall, running from one side of the foundation to the other. When properly spaced, these horizontal struts can even serve as framing for a basement.
Advantages of the Open Cut Method
The open cut method offers several significant advantages that make it a popular choice for many construction projects:
Cost-Effectiveness
For many projects, particularly those involving dense, sturdy soil, the open cut method can be the most economical approach to basement construction. The open cut slope method is especially cost-effective as it requires only the simplest forms of structural engineering and eliminates the need for expensive retaining walls.
Direct Access and Visibility
This method provides direct visual and physical access to the construction site, allowing for accurate assessment, repairs, and installations. The improved visibility also enables better control over the construction process.
Versatility
Open cut excavation can be used for a wide range of utility types, including water, sewer, gas, electric, and telecommunications infrastructure. The cantilevered open cut approach, in particular, offers considerable versatility and can be combined with bracing or anchors to accommodate large, ambitious buildings with multi-level basements.
Familiarity and Simplicity
As a well-established technique, many construction workers and utility crews are familiar with open cut excavation, making it relatively straightforward to execute. The construction process is simpler compared to other methods, especially for shallow buried tunnels and underground structures.
Faster Construction Progress
Since the surface is completely exposed, the transportation and installation of construction equipment and materials become more convenient, potentially accelerating the construction speed.
Easy Concealment
Using a cut and cover method-where excavated material is backfilled on top of a slope-you can effectively cover the hole created by an open cut excavation.
Disadvantages of the Open Cut Method
Despite its many benefits, the open cut method also comes with certain limitations and drawbacks:
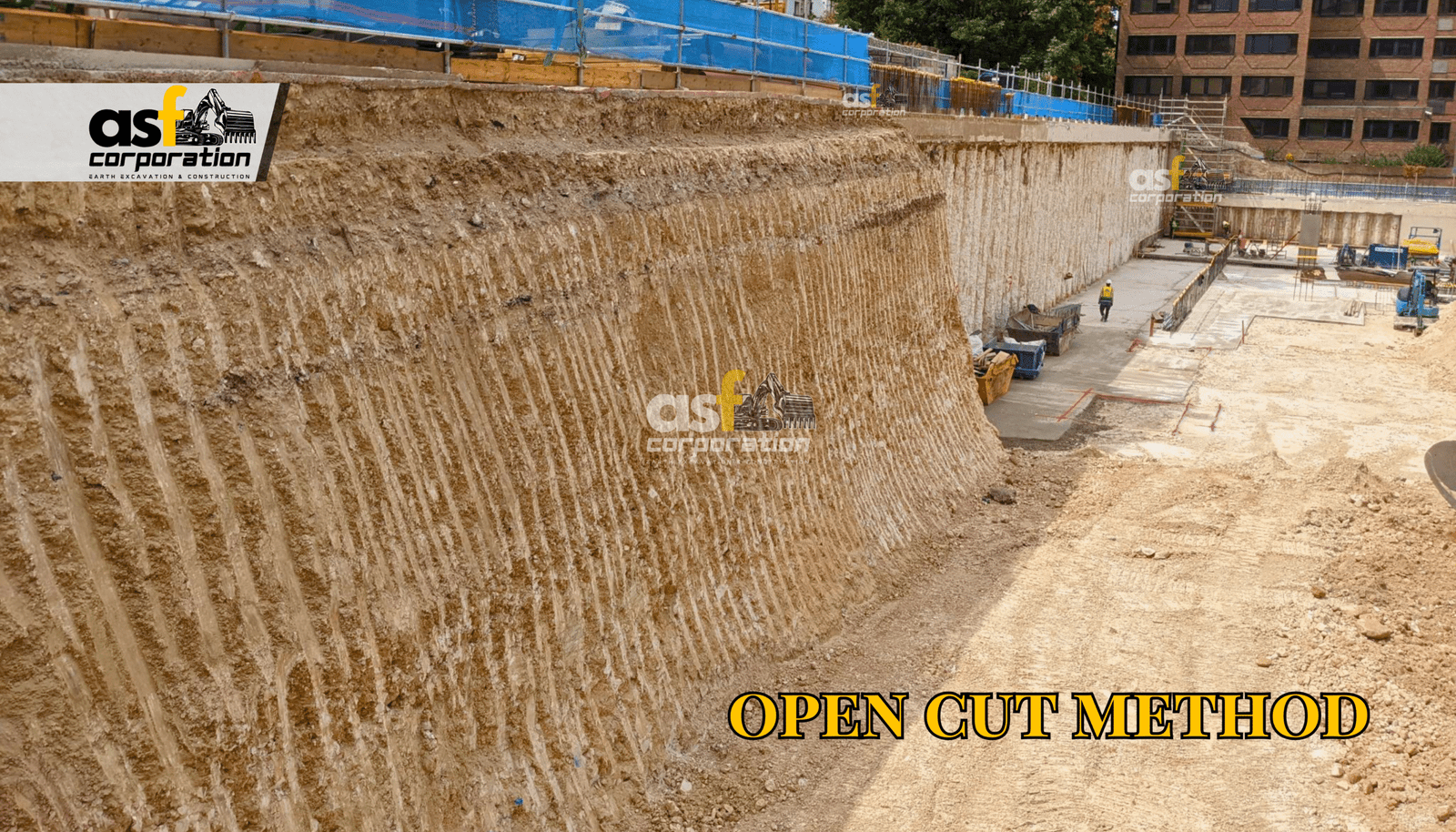

Environmental Impact
Surface excavation can significantly impact the surrounding environment, especially in densely populated urban areas. This may result in traffic disruptions, noise pollution, and dust contamination. The carbon footprint is also greater due to the use of heavy machinery and dump truck trips compared to trenchless methods.
Limited Application Scope
The open-cut method is primarily suitable for shallow buried projects and is not appropriate for deep buried tunnels and underground structures. Additionally, not all plots of land can be neatly excavated using this method. Buildings set on slopes may require a system of anchors and creative foundations to properly secure the structure.
Potential Surface Subsidence
If the construction process is not properly controlled, it may cause surface subsidence and affect the safety of surrounding buildings.
Slower Than Some Alternatives
Compared to top-down construction, which tackles upward building and basement excavation simultaneously, the open cut method can be slower. However, top-down construction is more complex and typically exceeds the budget of most residential homeowners.
Groundwater Issues
Open cut excavation can potentially cause problems with groundwater management during the construction process.
Extensive Material Handling
This method requires more excavation compared to trenchless alternatives. The excavated material must be safely disposed of at appropriate locations, necessitating multiple dumping trips that increase the project’s cost.
Restoration Requirements
The restoration of paved roads, sidewalks, landscaped lawns, and other surface features can significantly increase the overall cost of projects in developed areas.
When to Use the Open Cut Method
The open cut method is particularly well-suited for certain scenarios:
Shallow Basement Construction
The open cut slope method is ideal for one-story and two-story buildings with shallow basements. It provides a cost-effective solution while using basic physics principles to protect the foundation from collapsing soil.
Deeper Foundations with Proper Support
For taller buildings with deeper foundations and multi-level basements, the open cut cantilevered method with retaining walls offers an effective solution. Additional bracing systems can be implemented depending on the soil strength around the building.
Non-Paved Areas
Open cut methods are often preferred in areas that are not paved, as they represent a cheaper option. The surface can be easily restored by backfilling and planting seeds or sod.
Collapsed Pipe Repair
For pipes that have collapsed or lost their slope, the open cut method may be the only way to repair the damage, as the pipe will need to be removed and replaced.
Heavy Blockage Removal
This approach is the best option for pipes heavily blocked by roots and debris, as there’s no need to extract them from the pipe before repairs can begin.
Comparing Open Cut with Alternative Methods
When considering excavation methods, it’s important to understand how open cut compares with alternatives:
Open Cut vs. Trenchless Methods
Trenchless technologies have gained popularity over open cut methods in many applications because they offer several advantages:
- Reduced environmental impact
- Minimal disruption to traffic and pedestrians
- Lower carbon emissions
- Less social inconvenience (including vehicle traffic disruption, business and trade loss, site and pedestrian safety concerns, and pollution)
However, open cut methods still maintain advantages in certain situations, particularly in non-paved areas where they can be more cost-effective.
Open Cut vs. Top-Down Construction
Top-down construction tackles upward building and basement excavation simultaneously, making it faster than the open cut method. However, it’s more complex and typically exceeds the budget of most residential projects.
Implementing the Open Cut Method: Best Practices
To maximize the benefits of the open cut method while minimizing its drawbacks, consider these best practices:
Thorough Site Assessment
Before beginning any excavation, conduct a comprehensive assessment of the site conditions, including soil type, groundwater levels, and surrounding structures. This information will help determine whether the open cut method is appropriate and which variation (slope or cantilevered) would be most effective.
Proper Planning for Material Handling
Develop a detailed plan for handling and disposing of excavated materials. This should include identifying appropriate disposal sites and optimizing transportation routes to minimize costs and environmental impact.
Effective Water Management
Implement strategies to manage groundwater and surface water during excavation. This might include dewatering systems, drainage channels, or waterproofing measures.
Safety Measures
Ensure all necessary safety precautions are in place, including proper shoring, bracing, and protective barriers. Regular safety inspections should be conducted throughout the excavation process.
Minimizing Disruption
If working in developed areas, develop strategies to minimize disruption to traffic, businesses, and residents. This might include scheduling work during off-peak hours or implementing temporary traffic management plans.
Conclusion
The open cut excavation method remains a fundamental technique in construction and civil engineering, offering a balance of cost-effectiveness, simplicity, and versatility. While newer methods like trenchless technologies have emerged for specific applications, open cut excavation continues to be the preferred choice for many projects, particularly those involving shallow foundations in undeveloped areas.
By understanding the principles, advantages, and limitations of this method, construction professionals can make informed decisions about when and how to implement it effectively. Whether you’re building a residential home with a shallow basement or a larger structure requiring more complex foundation work, the open cut method offers proven solutions that have stood the test of time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the open cut method in construction?
The open cut method is an excavation technique that involves removing earth from a worksite to create space for a building’s foundation and basement. Unlike other methods, it prioritizes basement excavation first, with construction proceeding upward from there. It’s commonly used for shallow buried projects like tunnels or underground structures.
What are the two main types of open cut excavation?
The two primary types are the Open Cut Slope Method, which creates a natural slope from ground level to the foundation base, and the Open Cut Cantilevered Method, which uses retaining walls to support the excavation sides. The slope method is better for shallow projects, while the cantilevered approach suits deeper foundations.
When is the open cut method most appropriate to use?
The open cut method is most appropriate for shallow basement construction, projects in non-paved areas, collapsed pipe repairs, and situations requiring heavy blockage removal. It’s particularly cost-effective for one-story and two-story buildings with shallow basements.
What are the main advantages of using the open cut method?
Key advantages include cost-effectiveness (especially in dense soil), direct access and visibility to the construction site, versatility across various utility types, familiarity among construction crews, faster construction progress due to open access, and easy concealment through backfilling.
What are the limitations of the open cut method?
Limitations include significant environmental impact in urban areas, unsuitability for deep buried projects, potential surface subsidence, slower completion compared to some alternatives, challenges with groundwater management, extensive material handling requirements, and costly restoration needs in developed areas.
How does the open cut method compare to trenchless technologies?
Trenchless technologies offer reduced environmental impact, minimal disruption to traffic, lower carbon emissions, and less social inconvenience compared to open cut methods. However, open cut remains more cost-effective in non-paved areas and may be the only option for certain repairs like collapsed pipes.
What safety considerations are important when using the open cut method?
Important safety considerations include proper shoring and bracing, installation of protective barriers, regular safety inspections, effective water management systems, and adherence to local regulations regarding excavation depth and width.
How is groundwater managed during open cut excavation?
Groundwater is typically managed through dewatering systems, drainage channels, or waterproofing measures. The specific approach depends on the site conditions, including soil type and groundwater levels, which should be assessed before excavation begins.
What factors determine the cost of an open cut excavation project?
Cost factors include the excavation depth and width, soil type and condition, groundwater presence, disposal fees for excavated materials, transportation costs, restoration requirements, labor expenses, equipment rental, and any necessary permits or compliance measures.
How can environmental impact be minimized when using the open cut method?
Environmental impact can be reduced by optimizing transportation routes for excavated materials, implementing dust control measures, using modern equipment with lower emissions, scheduling work to minimize disruption, proper waste management, and thorough site restoration after project completion.
Ready to Start Your Next Excavation Project?
At ASF Corporation, we specialize in implementing the most effective excavation methods for your specific project needs. Our team of experienced professionals understands the nuances of different excavation techniques and can help you determine whether the open cut method is right for your construction goals.
Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our expertise can help you achieve a successful outcome.
ASF Corporation
Address: Vashantek, Dhaka Cantonment Dhaka-1206, Bangladesh.
Phone: +88 01907-636827
Email: info@asfcorporation.com
Don’t let foundation work delay your construction timeline. Reach out now to schedule a consultation and take the first step toward breaking ground on your project!



